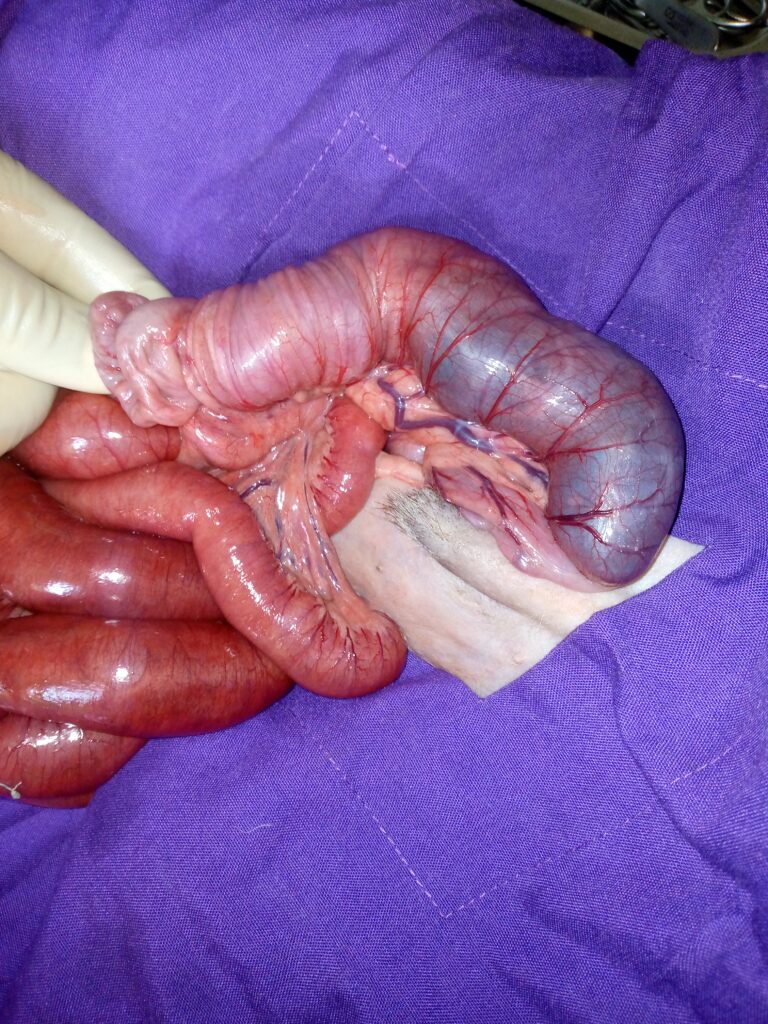
Is a disorder of the gastro-intestinal tract (GIT), which occurs when a segment of the intestines slides(telescopes) and enters into neighboring segment.
When this occurs, the intestinal lumen maybe completely blocked resulting into inability of the intestinal content to move from one portion to another. This can occur at any area along the GIT including the colon, cecum or stomach, though it mostly occurs at the ileo-cecol junction.
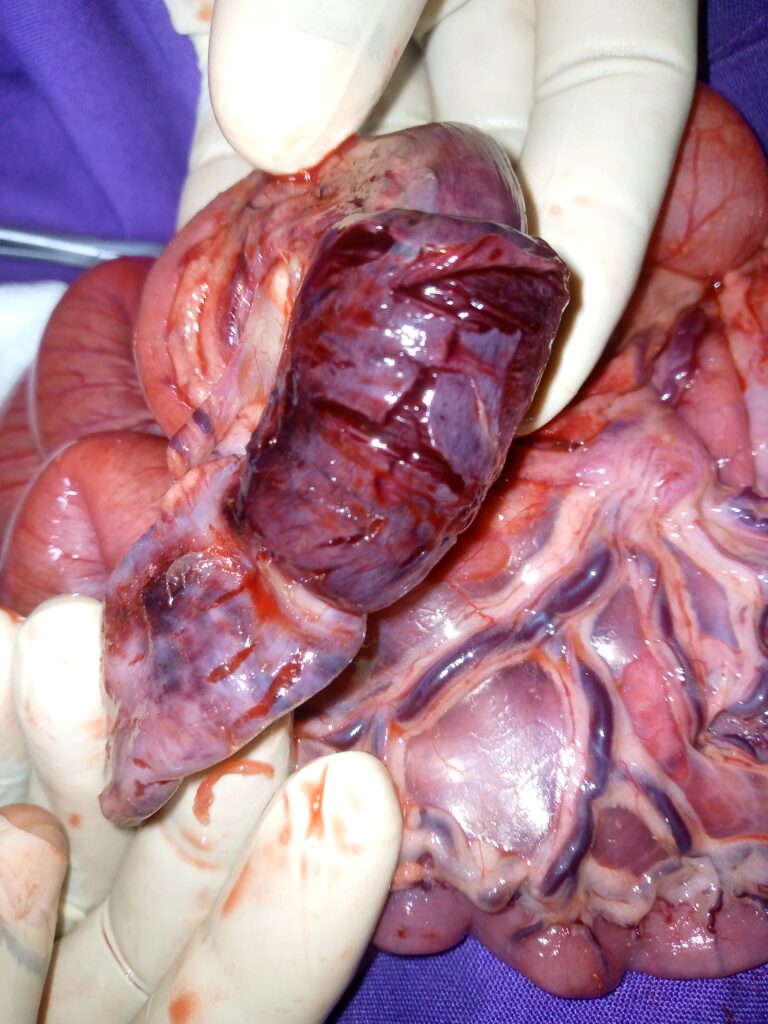
When there is obstruction, the affected part may undergo tissue damage resulting into perforation, endotoxaemia, hypovolemic shock and a life threatening peritonitis when the intestinal content leaks into the abdomen.
Causes of intussusception
- Intussusception is caused by any diversion from the normal GIT motility (irregular GIT movement). The irregularities can be caused by;
- Viral and/bacterial infections such as parvovirosis
- Intestinal parasites such as hook worms, whipworms and roundworms
- Traumatic injuries to the abdomen such as being hit by a car
- Tumors.
- Foreign bodies causing obstruction and inversion
- Abrupt changes in the deity
Clinical manifestation
Dogs with intussusception usually manifest with discomfort and abdominal pain(this is what owners usually report).
Other symptoms may include; diarrhea, vomiting, decreased appetite, bloody stool and hunched back.
Diagnosis
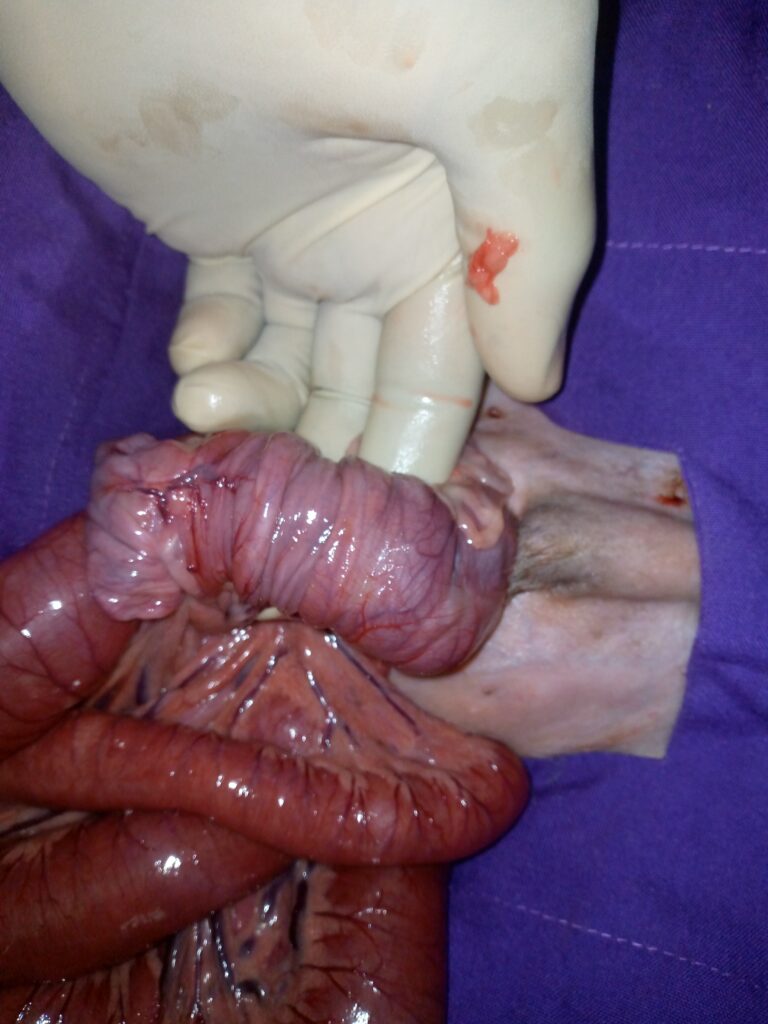
Physical examination by palpation of the abdomen may reveal a cylindrical mass
Radiograpy(X-ray)reveal an area of intestinal dilation though it may not confirm intussusception, contrast X-rays with barium can be done to confirm intussusception.
Ultrasounds can also be used to confirm intussusception
Treatment
Surgical collection with resection and anastomosis of the damaged area of the GIT