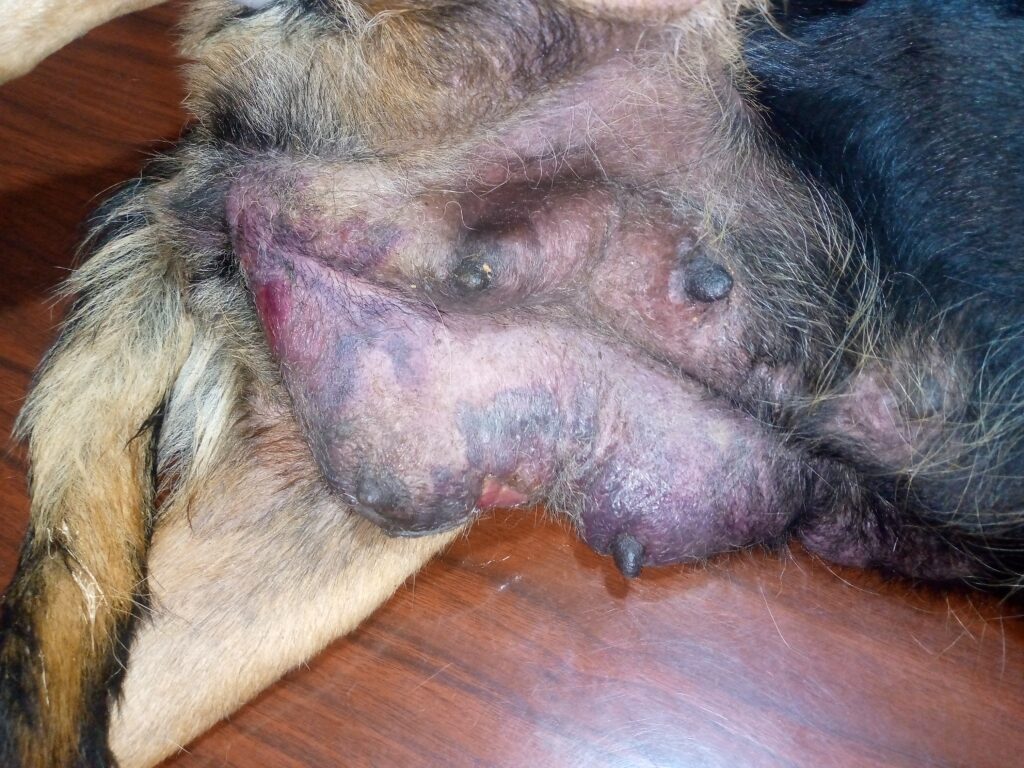
Mastitis is the inflammation of mammary gland tissues. It is mainly caused by bacteria e.g. E. coli, enterococci spp, staphylococcus, streptococcus and rarely by fungi
TYPES OF MASTITIS IN DOGS:- mastitis can be classified basing on the degree of inflammation and origin of the causative agent.
Based on origin of the causative agent:-
Environmental mastitis:- the pathogen is got from the surrounding environment where the bitch spends its time.
Contagious mastitis;- the pathogen is spread from one infected quarter to the other.
Based on the degree of inflammation;-
Clinical mastitis; evident abnormalities are noticed e.g. swollen, reddened, hot and painful mammary gland. Can further be grouped into per acute, acute, sub cute
Sub clinical mastitis;- no abnormalities are noticed but there is a severe reduction in the milk produced by the bitch.
Chronic mastitis;- persists for several months with abnormalities like swollen, hot, reddened and painful mammary gland that occur at irregular intervals.
Gangrenous mastitis;- the teats and the breast appear bruised, blood tinged milk and the skin sloughs off.
Symptoms of Mastitis
Signs of mastitis in a dog vary depending on nature and severity of the condition these include;-
- Swollen, painful and reddened mammary gland
- Drop / no milk produced
- Bruised skin of the teats and breast
- Clotted milk
- Blood tinged milk
- Bitch is reluctant to nurse the puppies
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
- Listlessness
PREDIPOSING FACTORS / RISK FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH MASTITIS IN DOGS;-
- Poor hygiene
- Abrupt weaning of puppies
- Damp environment
- Trauma
- Death of puppies
- Septicemic conditions
- Inbreeding
- First parity
DIAGNOSIS OF MASTITIS IN DOGS;- its detected using physical, imaging and laboratory tests;-
Physical tests;- these base on clinical signs of mastitis and the nature of the milk produced.
Laboratory tests;-
Milk cytology;- commonest method of detecting mastitis in dog . A small sample of milk is collected, examined under microscope for any pus cells / bacteria.
Bacterial culture and sensitivity; a sample of milk is collected uncontained by the external materials, put to conditions that favor growth of bacteria colonies then latter exposed to get the most effective antibiotics to use.
Imaging;- ultrasonography is done to rule out / in abscesses and tumors in the mammary gland.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF MASTITIS IN DOGS;-
- Mammary tumors
- Mammary abscess
- Edema of the mammary tissues
- Breast engorgement
- Galactocele
- Cellulitis
- Hematomas
- Rupture of the suspensory ligament
TREATMENT OF MASTITIS IN DOGS
The remedy protocol used vary basing on the nature, severity and primary cause of mastitis in dogs
The general treatment plan include;-
IV fluids for patients who are anorexic and dehydrated
Give broad spectrum antibiotics and anti-inflammatories
Surgical excision of dead mammary tissues
PREVENTION OF MASTITIS IN DOGS
- Proper hygiene
- Alternate puppies to different nipples to avoid engorgement of some quarters
- Clip the nails of the puppies
- Shave the hair around teats to avoid build up of bacteria
- Weaning should be done gradually
- Keep the nursing dog on clean and dry beddings 24/7.